Easy-to-prepare graphene oxide/sodium montmorillonite polymer nanocomposite with enhanced adsorption performance
Payam Arabkhani, Arash Asfaram*, Mohamed Ateia**
*Medicinal Plants Research Center, Yasuj University of Medical Sciences, Yasuj, Iran
**Department of Chemistry, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, 60208, USA
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101651
中文题目:易于制备的具有强化吸附性能的氧化石墨烯/钠基蒙脱土纳米复合材料研究
被引频次:据Web of science 分析检索结果显示,截至2023年5月15日该文章被引频次为59次。
Highlights
GO/NaMMT polymer nanocomposite was prepared by solution mixing-evaporation method.
The adsorption isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamic and mechanisms were studied in detail.
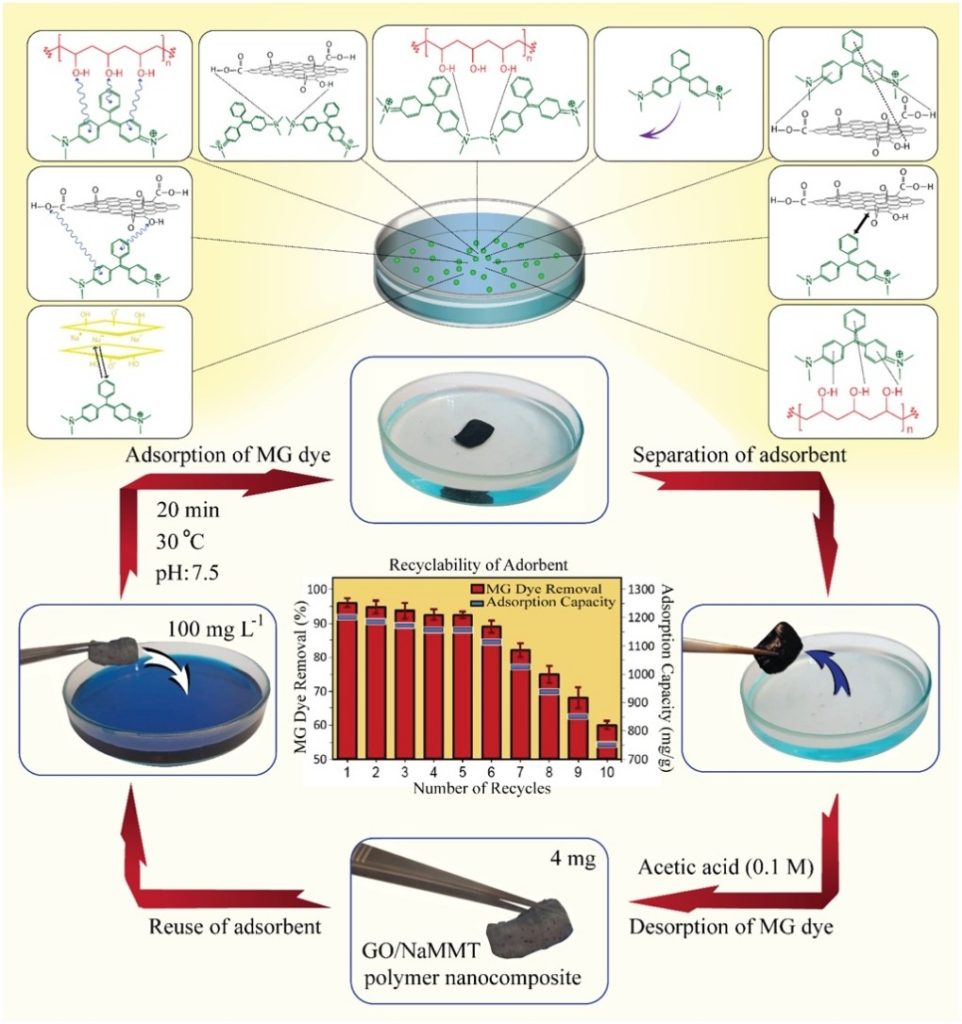
GO/NaMMT polymer nanocomposite showed high adsorption capacity of 1721 mg g−1 for MG dye.
The polymer nanocomposite was applied to treat six types of real water samples.
Abstract
A novel graphene oxide (GO)/sodium montmorillonite (NaMMT) polymer nanocomposite was synthesized using a simple and environmentally friendly solution-mixing-evaporation technique and characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and derivative thermogravimetric (DTG) analysis. The nanocomposite, as an efficient adsorbent with a surface area of 230 m2 g−1, was subsequently applied for the removal of malachite green (MG) dye from real wastewaters and the effects of MG initial concentration, contact time, solution pH, adsorbent dosage, and the solution temperature were thoroughly studied. The nanocomposite exhibited rapid MG adsorption by reaching to an equilibrium in 20 min and the adsorption process followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. Isotherm experiments showed good fitting to the Langmuir model, and the highest adsorption capacity of the GO/NaMMT polymer nanocomposite was 1721 mg g–1 at the temperature of 30 °C (approximately double the capacity of the highest previously reported adsorbent). Thermodynamic investigations disclosed that the process was inherently spontaneous and endothermic. Taken together, the proposed GO/NaMMT polymer nanocomposite, with the excellent properties, such as facile synthesis, cost-effectiveness (over five reusable cycles without any significant loss of its efficiency), effectiveness in real wastewaters, lack of production of secondary pollutions, stable three-dimensional (3D) structure (allow easy handling and separation during application), have high potential to serve as a highly efficient adsorbent for water/wastewaters treatment applications.
Keywords: Adsorption; Malachite green; Polymer nanocomposite; Real samples; Regeneration
文章链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2214714420305298
